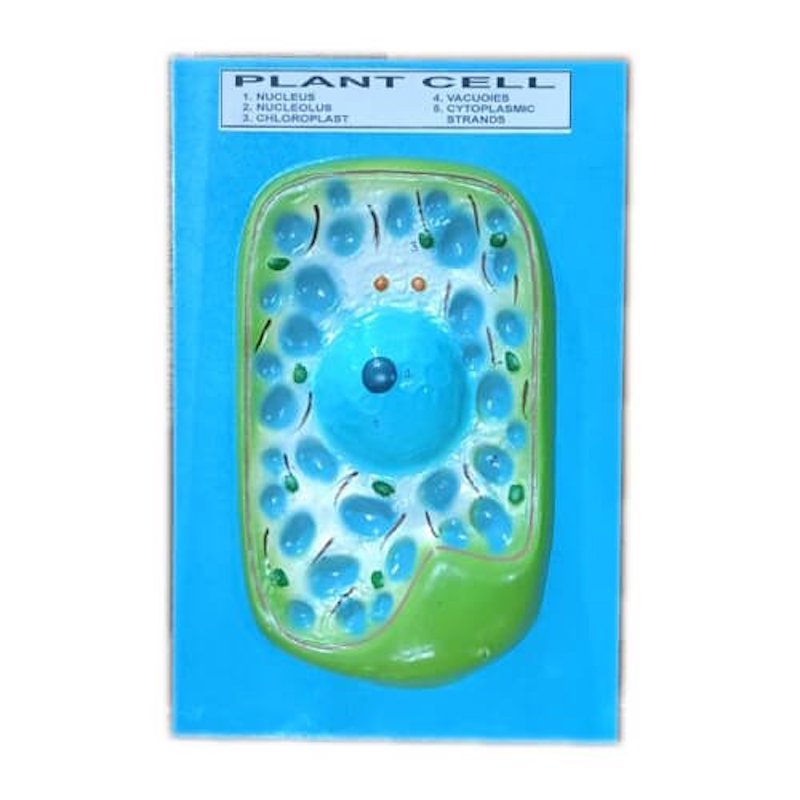
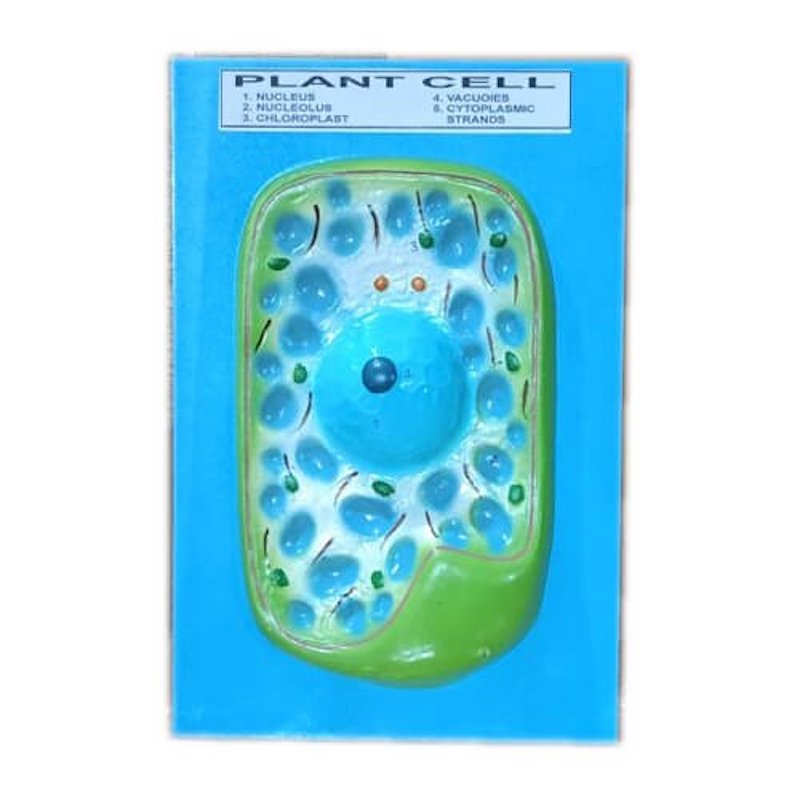
This is the Scientific Model of Plant Cell on Board for Education and Training.
\n
The Model of Plant Cell consists of
\n-
\n
- Nucleus \n
- Nucleolus \n
- Chloroplast \n
- Vacuoies \n
- Cytoplasmic Stranos \n
-
\n
- Plant Cell Model \n
- Ideal for Training & Education \n
- Made in India \n
Customer Questions and answers :
Login to ask a question
 Global Finds
Global Finds  Quick Commerce
Quick Commerce  Daily Bazar
Daily Bazar  Electronics & Appliances
Electronics & Appliances  Mother, Baby & Toys
Mother, Baby & Toys _20.png) Beauty
Beauty  Sports
Sports  Automotive
Automotive  Stationery, Books & Music
Stationery, Books & Music _20.png) Fashion Luxe
Fashion Luxe _20.jpeg) Home
Home  Garden & Pet Care
Garden & Pet Care  Special Weekly Offer
Special Weekly Offer  Grocery
Grocery  Global Finds
Global Finds  Quick Commerce
Quick Commerce  Daily Bazar
Daily Bazar  Electronics & Appliances
Electronics & Appliances  Mother, Baby & Toys
Mother, Baby & Toys _20.png) Beauty
Beauty  Sports
Sports  Automotive
Automotive  Stationery, Books & Music
Stationery, Books & Music _20.png) Fashion Luxe
Fashion Luxe _20.jpeg) Home
Home  Garden & Pet Care
Garden & Pet Care  Special Weekly Offer
Special Weekly Offer  Grocery
Grocery