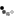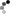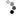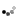- \n
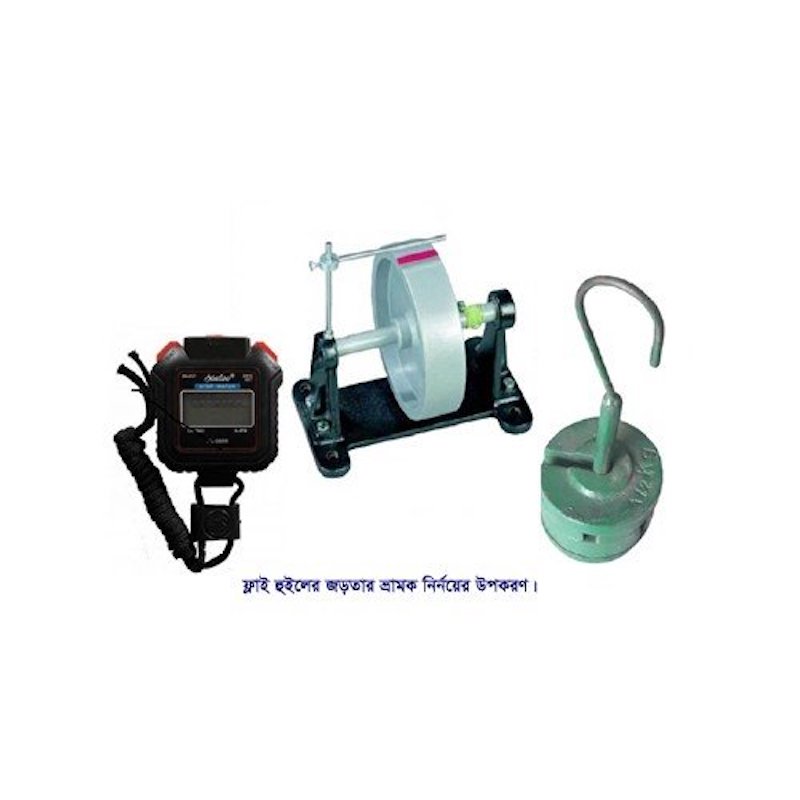
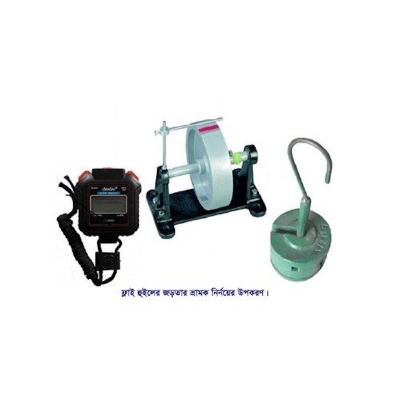
- To complete the physical test of “Misleading diagnosis of flywheel inertia," we offer the following items under this package. \n
- With fly flywheel counter -1 piece, 5kg of weight, 500 g with a hook -1 piece, Stop Watch Digital is guaranteed for 10 years -1 piece. \n
\n
\n
\n
\nA misleading diagnosis of flywheel inertia refers to an incorrect assessment of a flywheel's rotational mass and its impact on a system's performance. This can lead to various issues like inadequate energy storage, instability, or unnecessary cost and weight in the design. \n
\n\n
\n\n
\n\n
\n
\n\n
\n
\n
\nHere's a more detailed explanation:
\n\n
\n
\n
\nWhat is Flywheel Inertia?
\n\n
\n
\n
\nA flywheel is a rotating mechanical component designed to store energy and stabilize the rotational speed of a machine. Its inertia, or resistance to changes in rotational motion, is a critical factor in its effectiveness. Accurate measurement of this inertia is essential for proper system design and operation. \n
\n\n
\n\n
\n\n
\n
\n\n
\n
\n
\nHow can the diagnosis be misleading?
\n\n
\n
\n
\nMisleading diagnoses can arise from several factors:
\n\n
\n
\n
\n- \n
- \n
\n\n\n\n\nIncorrect Calculations:\nErrors in mathematical formulas or assumptions about the flywheel's geometry, mass distribution, or material properties can lead to inaccurate inertia calculations, according to some online sources. \n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n
\n
- \n
\n\n\n\n\nOutdated or Inaccurate Data:\nUsing outdated or imprecise data on material densities or dimensions will also result in faulty calculations. \n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n
\n
- \n
\n\n\n\n\nMeasurement Errors:\nInaccurate measurements of the flywheel's dimensions, mass, or rotational speed during experiments will contribute to inaccuracies. \n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n
\n
\n
\n
\n
\nConsequences of Misleading Diagnosis:
\n\n
\n
\n
\n- \n
- \n
\n\n\n\n\nUnderestimated Inertia:\nLeads to insufficient energy storage, causing the flywheel to slow down too quickly and impacting the machine's performance. \n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n
\n
- \n
\n\n\n\n\nOverestimated Inertia:\nResults in excessive energy storage, leading to a larger, heavier, and more expensive flywheel than necessary. \n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n
\n
- \n
\n\n\n\n\nSystem Instability:\nMay cause vibrations, erratic behavior, or even failure of the system. \n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n
\n
- \n
\n\n\n\n\nInefficient Design:\nMisleading diagnoses can result in designs that are not optimal for the intended application. \n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n
\n
\n
\n
\n
\nImportance of Accurate Diagnosis:
\n\n
\n
\n
\n- \n
- \n
\n\n\n\n\nPerformance Optimization:\nProper inertia assessment ensures the flywheel functions as intended, providing the required energy storage and stability.\n
\n
- \n
\n\n\n\n\nCost-Effectiveness:\nAccurate inertia calculations help in designing the most efficient and cost-effective flywheel for the application.\n
\n
- \n
\n\n\n\n\nSafety:\nAccurate diagnosis is crucial for ensuring the safe operation of machinery by preventing instability or component failure.\n
\n
- \n
\n\n\n\n\nTroubleshooting:\nProvides insights into potential problems with flywheel systems, aiding in troubleshooting and maintenance.\n
\n
1 Set the instrument for flywheel inertia
Customer Questions and answers :
Login to ask a question
 Global Finds
Global Finds  Quick Commerce
Quick Commerce  Daily Bazar
Daily Bazar  Electronics & Appliances
Electronics & Appliances  Mother, Baby & Toys
Mother, Baby & Toys _20.png) Beauty
Beauty  Sports
Sports  Automotive
Automotive  Stationery, Books & Music
Stationery, Books & Music _20.png) Fashion Luxe
Fashion Luxe _20.jpeg) Home
Home  Garden & Pet Care
Garden & Pet Care  Special Weekly Offer
Special Weekly Offer  Grocery
Grocery  Global Finds
Global Finds  Quick Commerce
Quick Commerce  Daily Bazar
Daily Bazar  Electronics & Appliances
Electronics & Appliances  Mother, Baby & Toys
Mother, Baby & Toys _20.png) Beauty
Beauty  Sports
Sports  Automotive
Automotive  Stationery, Books & Music
Stationery, Books & Music _20.png) Fashion Luxe
Fashion Luxe _20.jpeg) Home
Home  Garden & Pet Care
Garden & Pet Care  Special Weekly Offer
Special Weekly Offer  Grocery
Grocery