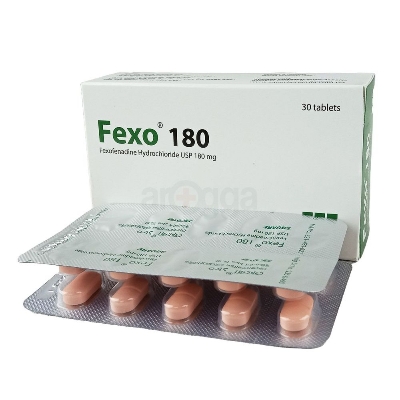
Fexo 180mg 1 Strip
Introduction
Fexo 180 belongs to a group of medicines called antihistamines. It is used to treat various allergic conditions such as hay fever, conjunctivitis and some skin reactions such as eczema, hives and reactions to bites and stings. It also relieves watery eyes, runny nose, sneezing, and itching. Fexo 180 should be taken on an empty stomach. The dose may vary depending on what you are taking it for. Take it as prescribed by your doctor. You may need this medicine only on days you have the symptoms, or you may need to take it every day to prevent the symptoms from happening. If you stop taking it earlier than advised, your symptoms may come back. This medicine is generally very safe. The most common side effects include headache, drowsiness, dizziness, and nausea. These are usually mild and go away after a couple of days as your body adjusts. Consult your doctor if any of the side effects persist or worry you. Before taking it, tell your doctor if you have any problems with your liver or kidneys or with your heart as antihistamines can cause your heart to beat faster. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also consult with their doctor before taking it. Avoid drinking alcohol as it can cause excessive drowsiness with this medicine. It usually does not impair your ability to drive, but you should not drive if it makes you feel sleepy or dizzy.
Uses of Fexo 180
- Allergic conditions
Side effects of Fexo 180
Common
- Headache
- Drowsiness
- Nausea
- Dizziness
How to use Fexo 180
Take this medicine in the dose and duration as advised by your doctor. Swallow it as a whole. Do not chew, crush or break it. Fexo 180 is to be taken empty stomach.
How Fexo 180 works
Fexo 180 is an antihistaminic medication. It treats allergy symptoms such as itching, swelling, and rashes by blocking the effects of a chemical messenger (histamine) in the body.
Quick Tips
- Fexo 180 is an antihistaminic medication. It treats allergy symptoms such as itching, swelling, and rashes by blocking the effects of a chemical messenger (histamine) in the body.
- It is less likely to make you feel sleepy than some other similar medicines.
- Do not take it with any fruit juices (such as apple, orange, or grapefruit) as they might make the drug less effective.
- It may cause nausea. Stick to simple meals, and do not eat rich or spicy food.
- Avoid using antacids 30 minutes before or after taking this medicine. It can make it harder for your body to absorb this medication.
Brief Description
Indication
Allergic rhinitis, Hay fever, Urticaria, Allergy
Administration
Should be taken on an empty stomach. Take before meals. Do not take w/ fruit juice.
Adult Dose
Adults: Allergic rhinitis: 120 mg once daily or 60 mg twice daily Urticaria: 180 mg once daily
Child Dose
Children: Tablet 2-12 years: 30 mg (1 spoonful) or 5 ml twice daily 6 months-2 years: 15 mg (1/2 spoonful) or 2.5 ml twice daily >12 years: 60 mg PO BID OR 180 mg PO qDay ODT 6-12 years: 30 mg PO BID
Renal Dose
Adult: Initially, 60 mg once daily. Child: 6 mth-<2 yr: 15 mg once daily and 2-11 yr: 30 mg once daily. >12 years: 60 mg PO qDay, initially
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity.
Mode of Action
Fexofenadine, an active metabolite of terfenadine, is a competitive peripheral histamine H1-receptor antagonist on effector cells in the GI tract, blood vessels and respiratory tract.
Precaution
Renal impairment. Pregnancy, lactation; children <6 yr. Lactation: Excretion in milk unknown; use with caution (AAP states “compatible with nursing”)
Side Effect
>10% Vomiting (6-12%) 1-10% Headache (5-10%),Cough (4%),Diarrhea (3-4%),URTI (3%),Back pain (2-3%),Pyrexia (2%),Dysmenorrhea (2%),Dizziness (2%),Stomach discomfort (2%),Pain in extremity (2%),Somnolence (1-3%),Rhinorrhea (1-2%)
Pregnancy Category Note
Pregnancy category: C Lactation: Excretion in milk unknown; use with caution (AAP states “compatible with nursing”)
Interaction
Co-admin with ketoconazole or erythromycin may increase plasma levels of fexofenadine. May increase adverse effects of other anticholinergics and CNS depressants. May increase arrhythmogenic effect of antipsychotic agents (phenothiazines); avoid concurrent usage. May reduce the efficacy of betahistine. Pramlintide may increase the anticholinergic effect of fexofenadine. Bioavailability may be increased by verapamil. Efficacy may be reduced by rifampin.
Note:
*Product color and design may slightly vary due to new design upgradation.
*Product delivery duration may vary due to product availability in stock.
Disclaimer: The color of the physical product may slightly vary due to the deviation of lighting sources, photography or your device display settings.
Customer Questions and answers :
Login to ask a question

 Othoba Trending Store
Othoba Trending Store  Food & Grocery
Food & Grocery  Electronics
Electronics  Toys & Baby Products
Toys & Baby Products  Bags, Wallets & Belts
Bags, Wallets & Belts  Special Weekly Offer
Special Weekly Offer  Fashion
Fashion  Building Materials
Building Materials  Home & Living
Home & Living  Stationery, Books & Music
Stationery, Books & Music  Riding, Sports & Fitness
Riding, Sports & Fitness  Othoba Trending Store
Othoba Trending Store  Food & Grocery
Food & Grocery  Electronics
Electronics  Toys & Baby Products
Toys & Baby Products  Pharmacy
Pharmacy  Home & Living
Home & Living  Stationery, Books & Music
Stationery, Books & Music  Riding, Sports & Fitness
Riding, Sports & Fitness